General information about TPMS
What is TPMS?
- TPMS abbreviation stands for: Tyre Pressure Monitoring System
- TPMS is a built-in monitoring system for the tyre pressure in motor vehicles
- Automatic and direct indication as a warning on the display when a problem occurs in one or more tyres due to a pressure loss
Aim:
- Increase the driving safety and reduce accidents, since incorrect tyre pressures increase the braking distance, the cornering performance can be affected and the tyres can heat up.
- Prevention of the increased fuel consumption due to less than optimal tyre pressures.
- Reduction of tyre wear due to higher rolling resistance as well as of CO2 emissions.
Advantages:
- Tyre pressure problems will be shown immediately to the driver.
- The problems can be resolved at an early stage.
- No more need for manual air pressure checks
Timescale for the equipping with TPMS:
- Since the 1st November 2012 all types of new motor vehicles and mobile homes sold in the EU must be equipped with a TPMS.
- From the 1st November 2014 all motor vehicles and mobile homes in the EU must have a TPMS at initial registration.
What capabilities must the TPMS have?
Already in the vehicle manufacture a direct or indirect TPMS must be integrated, a subsequent equipping is considered as not conforming.
Characteristics of the TPMS according to EU law:
- Warning in the event of pressure loss in an individual tyre (within 10 minutes):
20% lower than operating pressure (Pwarm) at 1.5 bar
- Warning in the event of pressure loss in all four tyres (sudden and creeping loss):
20% lower than operating pressure (Pwarm) at 1.5 bar
- Determination of pressure loss at speeds of 40 km/h to the maximum driving performance of the vehicle
- Data transfer on 434 MHz
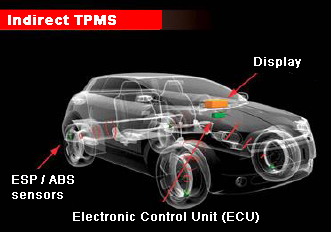
What is indirect TPMS?
Use of existing sensors of the ESP/ABS by identifying the tyre pressure via the tyre speed and send the data to the central control unit (ECU = Electronic Control Unit)
In the event of pressure loss:
- Determining an increased speed of the tyre by the system
- Indication on the display as a warning to the driver
Compared with the direct TPMS:
- imprecise (e.g. no indication of the exact pressure loss and temperature measurement)
- less convenience (e.g. no measurement of the tyre pressure when the vehicle is at a standstill)
- no extra effort/cost when changing tyres, since no sensors in the tyres need to be borne in mind
What is direct TPMS?
Tyre pressure monitoring system with the help of sensors in each tyre, which measure the pressure and temperature, send the data collected via radio to a central receiver, data processing, indication on the display for the driver
Compared with the indirect TPMS
- very precise data collection
- additional functions, such as a tyre position detection, the measurement of a pressure loss when stationary and the monitoring of the spare wheel
- significant additional costs for maintenance and tyre change
- requires significant changes for workshops, for example in maintenance, installation and programming of TPMS sensors
- Equipping all tyres (winter tyres, summer tyres, spare tyres) with a functional sensor

What areas do the TPM systems effect?
In the following situations the vehicle owner or workshop visited come into contact with the direct TPMS:
- Diagnosis when the warning light comes on in the display
- Maintenance, repair or replacement of sensors
- Changing tyres
- Tyre fitting
- Set of complete wheels
- Tyre repairs
- Service check (e.g. main inspection for TÜV (German MOT))
Consequences for the vehicle owner/keeper:
Because of the complex technology of the TPMS it becomes even more difficult for the owner/keeper to carry out a tyre service themselves. On illumination of the warning signal (e.g. defective tyres or faulty sensor) and when changing tyres they need a workshop with the appropriate service.
Consequences for the workshop:
It is therefore absolutely necessary for workshops, to prepare themselves for the new technology and to take early measures to be able to serve customers with a vehicle with TPMS and to position themselves as specialists in this area of the market.
Today there are numerous vehicles on the market with a direct TPMS, which is why workshops already before the 1st November 2014 are confronted with the software and the service demands of the customer.
In the next few years, the concentration of TPMS in vehicles will continue to increase. All of these vehicles have a need for replacement sensors or sensors for the fitting on winter tyres, which result in a huge sales potential of the relevant deliverables for the workshops.
In addition to the necessary know-how workshops will also need the appropriate tools (e.g. to diagnose problems or to program the sensors) and spare parts (e.g. seals, valves or entire sensors).
Information for fitting partners
What changes to the work processes of the tyre service result from TPMS?
- Maintenance of the sensors in the wheels of a vehicle with direct TPMS at each wheel change
- To prevent corrosion of the valve and the sensor: renewal of the wearing parts valve core, nut, seal and cap by special service kits

- Determine the battery charge using diagnostic/proprietary programming tools
- Replace weak/flat batteries because of the finite battery life of a sensor (varies between 4 to 10 years)
- Analysis and correction of problems indicated on the display by the illumination of the warning light (in the event of loss or failure of a sensor, e.g. flat battery, corrosion or the sensor breaking off the valve)
- As a non-functional TPMS is evaluated as a minor fault during the main inspection according to section 29 of the German Road Traffic Licensing Act and must be rectified immediately by the owner/keeper, the workshop must be able to rectify these faults.
Recommendation for the workflow, if the customer wants a diagnosis and problem resolution if the warning lamp lights up, maintenance of their TPMS, or a tyre service (e.g. tyre change, assembly/disassembly): 
- Check the warning light and the indication in the display of the vehicle - if the lamp is lit a diagnosis is required, whether there is a system error or a air leak (cf. vehicle book)
- Check the valve (Is the seal damaged? is there corrosion?)
- Scanning of sensors by a diagnostic/programming tool
- Documentation of the results of the scanning (input state of the TPMS of the vehicle)
- Execution of the customer order e.g. wheel change, renewing the tyres or sensors, maintenance of the valve. If required: Training of the (new) sensors on the vehicle and checking the TPMS.
- Documentation of the initial state of the TPMS of the vehicle (state of the TPMS may not be worse/less than the input state) and inform the customer
Please note: As a functional TPMS is part of the operational approval, the workshop must guarantee the functionality after each operation. Corresponding documentation of the condition of the TPMS before and after performing the maintenance, diagnostics and the customer order therefore constitutes a safeguard in the framework of liability and warranty.
What is required for TPMS? What investment needs to be made?
To prepare for customers with a direct TPMS in the vehicle, the following measures are necessary:

- Sufficient stocks of vehicle-specific original, or unprogrammed universal sensors
- Sufficient stocks of valves and service kits of the necessary spare parts during tyre changes for the maintenance of the sensors (valve core, cap, nut, seal)
- Special tools such as valve screwdriver for the correct torque of valve core
- Diagnostic/programming tools for problem diagnosis, for programming and training, if necessary, of sensors and the central control unit
- Trained personnel as a prerequisite for the professional installation/dismantling of wheels on a vehicle with direct TPMS
Advantages and disadvantages of TPMS for workshops
|
Advantages
|
Disadvantages
|
|
- Additional income from the new services (e.g. extra tyre service, TPMS maintenance) and spare parts (for example, new sensors, service kits).
- Customers with a direct TPMS with summer and winter tyres come at least 2x a year in the workshop
- Improving the customer relationship with this regular contact with customers and the possibility to offer additional services
|
- Lengthening of the handling time required for a vehicle with direct TPMS
- During peak season the problem is to be solved, of being able to handle fewer orders per day because of the extra time overhead.
Solution: Compensate for the increased time spent through good preparatory work, such as telephone consultation about the customer orders or timely provision of material
|
|
- Increase in the importance of workshops for a tyre service (e.g. the vehicle owner cannot undertake tyre change with direct TPMS readily themselves)
|
- Customers can be deterred by the increased prices or are not willing to pay, with the result of the reduction of tyre sales to all-season tyres or foregoing TPMS maintenance
Solution: Better understanding of the additional costs incurred by good customer advice and information about TPMS with reference to the statutory provisions as well as the emphasis on safety aspects
|
|
- Specialisation as TPMS workshop as a competitive advantage through differentiation of services offered, know-how and service.
|
- Error rates for the handling of the TPMS technology by a lack of know-how can lead to a bad reputation and claims for damages
Solution: Qualification of the staff by self-training, training or instruction, good information sharing, and communication among the employees to promote know-how
|
Which sensors can be used for the TPMS (e.g. as a replacement for a faulty sensor)?
Each manufacturer can use a different sensor type for the original equipment of the vehicles. For this reason, there are now over 150 different sensor models on the market.
Requirements:
- The sensors to be installed must be pre-programmed for the vehicle
- Vehicle and sensor must be compatible, i.e. not every sensor can be installed in any vehicle
- In the case of replacing a sensor or for winter tyres/spare tyres is an option to use either original sensors or unprogrammed universal sensors.

Original sensors are already pre-programmed with the vehicle-specific details, the sensor can therefore only be used in some specific vehicles. Due to the wide variety of different sensors, it would significantly increase the stock levels and the capital tied up (of the most important original sensors should always be at least 4 units in stock) of the workshop, in order to be able to serve the customer satisfactorily.
Unprogrammed universal sensors are not pre-programmed and can be integrated into most vehicles without any problems. There is therefore no need for a variety of sensors, such as in the original sensors, in order to be able to serve all customers needs (a basic stock of universal sensors is enough). However, in addition to the universal sensors a special programming tool is needed to be able to program the sensors specifically for the vehicle. Via this tool in the first step, the technical specifications of the vehicle are queried and the position of the tyre, in which the sensor is located which is to be programmed (e.g. front left). Subsequently the original sensor is detected by the programming device (depending on the software e.g. by entering the sensor ID or automatic capture by inserting the original sensor) and the collected data is used for the programming of the new sensor. Imitates the original sensor, as it were. If no original sensor should be available, a new sensor ID can also created on the programming tool.


Summary of the preparations for TPMS
The TPMS obligation presents the workshops, particularly in view of the technology of the direct TPMS with many changes and challenges. The development in the market in terms of the dissemination of the TPMS is very positive, which is why at an early stage preparation for the technologies is an advantage.
In the preparations for the work with the direct TPMS the following points are helpful:
- Good preparation for the customer discussions (ascertaining the vehicle data, direct/indirect TPMS, information about TPMS, negotiation and the justification of the extra costs).
- Preparation of the staff for the new technology
- Investment in appropriate sensors and diagnostic programming tools
- Use of competitive advantages by communicating the TPMS services to customers
- Optimisation and adaptation of the internal processes in tyre service
- Adjustment of the lead times and prices for the tyre service for vehicles with direct TPMS
- Documentation of the condition of the TPMS before and after the work
How can your staff prepare for the new requirements of TPMS?
Through the direct TPMS changes are coming to the workshops in the work processes for maintenance or tyre service.
It is important to prepare the employees for these changes, in order to ensure that all customers can be served properly and no errors take place in the advice and handling of TPMS. It is recommended, that employees take part in special training, to learn how to work with TPMS. There are many different providers of TPMS training.
How are the sensors installed in the wheel?
For the installation of the sensors a special tool is required for professional installation or disassembly. These tools simplify the assembly/disassembly of the sensors and ensure that nut and valve for the sensor holder are attached with the correct torque.
The sensors are mounted within the tyre on certain tyre valves:

For the mounting you can choose between an aluminium and a snap-in valve (rubber valve), with special versions of sensors for both kinds of valve (ensure compatibility of valve and sensor). A snap-in valve is usually cheaper and easier to install than an aluminium valve. However, due to the centrifugal forces acting up to a maximum speed of 210 km/h a snap-in valve is not usable, an aluminium valve must be used for these high speeds. Whenever a tyre is changed maintenance of the valve should take place in which the valve core, valve cap, nut, washer and seal are replaced. For this maintenance there are special kits, which contain the required spare parts.
Snap-in valve: 
- Sensor
- Rubber valve
- Torx screw (self-tapping)
- Valve insert (nickel plated)
- Valve cap (plastic)
Aluminium valve: 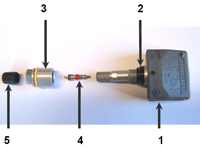
- Valve, with moulded sensor housing
- Rubber seal
- Gland nut
- Valve insert (nickel plated)
- Valve cap (plastic)
What changes will there be for the customer contact?
Customers must be informed about:
- The technology and the demands of the TPMS
- The higher time needed for the tyre service in TPMS vehicles
- The higher prices for the tyre service with TPMS
- Setting up an appointment to determine whether or not the vehicle has direct TPMS.
- Creating a timetable (calculation of the extra expense involved in tyre assembly with TPMS).
- Preparation of required spare parts (e.g. replacement sensors or service kits).
Qualification / training of employees:
- Clear communication of the operating principle of the TPMS to the customer.
- For the customer understandable explanation of the specifics in tyre servicing.
- Inform the customer of all of the changes made
- Documentation of input and initial status of the TPMS.
- Verifiable reasons for the customer for the higher price of the tyre service due to the additional expenses (time, know-how, technical devices such as the programming tool, servicing the valves and sensors).
How does the vehicle recognise the (new) sensors?
After the sensors have been programmed and installed in the wheel, it must be ensured that the vehicle also detects the sensor and the communication between the sensor and readout device works. This requires that the sensors of the central receiver (control and data processing unit of the TPMS) are activated, when a new sensor ID is used/created or the original wheel position of the sensor has been changed.
There are three types of training/programming for a new sensor (depending on the capabilities of the vehicle):
- Self-training of the vehicle: During a 10-minute drive at a speed between 35-100km/h the vehicle reads the sensor automatically, the warning light goes out automatically (e.g. for Mercedes, Vauxhall/Opel, VW, Ford, Mazda, Hyundai).
- Manual teach-in by vehicle owner/keeper over the vehicle menu: A given process, which can be referred to in the vehicle manual (e.g. for Audi, Mercedes, BMW, Porsche).
- Teach-in on certain programming/diagnostic tools: The sensors are taught by building a connection between the programming tool and the OBDII interface (= On Board Diagnostic interface) (e.g. for Renault, Citroen, Peugeot, Nissan, Vauxhall/Opel, Fiat and Lancia). This interface is also used for example in problem diagnosis when the warning lamp is lit.
What must be observed when ordering or producing your own set of complete wheels?
In the case of a vehicle fitted with direct TPMS, note the following:
- Since all tyres must be equipped with sensors, a sensor is to be built into this vehicle for a set of complete wheels.
- Original sensors are already programmed vehicle-specifically and can be fitted without further programming in the wheel and then mounted on the vehicle.
- Universal sensors, however, need a programming by a special diagnostic/programming tool, to transmit vehicle-specific details to the sensor and therefore to be compatible with the TPMS of the vehicle. Depending on which programming tool the workshop has invested in, the sensors must be programmed before the production of the complete wheels or can be subsequently programmed via radio.
What programming/diagnostic tools are there for TPMS?
There are different types of programming/diagnostic tools with many different functions ranging in price from 500-1500 EUR.
For a diagnosis, the tools make contact with the sensors via radio, so that the fault in the TPMS is shown on the tool display. Typically, only devices of the upper price range have the functionality to produce a direct interface with the OBD and teach in new sensors over it. For the programming of the universal sensors with the typical vehicle data and a cloned or newly created sensor ID a programming tool is unavoidable. It is even possible with some tools, to establish contact via radio with sensors already built-in and to subsequently program them.

- Pre-service tools: Primarily serve for diagnosis (partly with programmable capability), have a small display, data can be transferred to a PC via USB, thought of rather as an entry-level system with a few occasional diagnoses (and programming).

- PAD (Programming Accessory Devices): Read out and programming of sensors, which must be in direct contact with the PAD (insertion of the sensor), the PAD is connected to a PC via USB, which serves as a display.

- All-In-One: Programming by radio in a matter of seconds by the limiting of existing sensors IDs, or creating a new ID, simple and quick diagnosis by radio, can often create an OBD interface, data can be automatically transmitted to a PC) (additional functions such as printing reports), recommendation for average visited workshops.
Information for complete wheel customers
When will the TPMS obligation affect me?
You drive a motor vehicle or a motor home. Then you need to know the following:
- Since the 1st November 2012 all types of new motor vehicles and mobile homes sold in the EU must be equipped with a TPMS.
- From the 1st November 2014 all motor vehicles and mobile homes in the EU must have a TPMS at initial registration.
Why should tyre repairs not be carried out by breakdown assistants themselves in the case of direct TPMS?

Through the use of breakdown assistants, such as aerosol sprays, it can lead to chemical reactions, which damage the sensor and the tyres.
Where can I get the technology?
An indirect or direct TPMS is already installed during the manufacture of the vehicle. If the manufacturer should not install TPMS in the vehicle, retrofitting is not necessary, because then the vehicle is not subject to the TPMS obligation.
A workshop that offers the TPMS service can help you regarding spare parts such as a service kit for the valve maintenance or a replacement sensor.
Please note that due to the complex technology of the TPMS a specialist workshop, which has the appropriate speciality or programming tools, for tyre changes, maintenance work and in the event of problems (e.g. warning on the display) is to be recommended.
What if I want /need to change a tyre (breakdown, wear, winter /summer tyres)?
During a tyre service in the case of a direct TPMS the sensor must always be checked.
Vehicles, which are subject to the TPMS obligations, must fit all the tyres with sensors.
If a new tyre should be installed on the vehicle, a sensor which is compatible with the TPMS must also be installed in the vehicle.
Can I install my tyres with direct TPMS myself?
For a direct TPMS please note the following during tyre service:
- Need for the maintenance of the valve each time a wheel is changed, in order to prevent wear of the sensor
- On new tires: new teach-in of the sensors on the vehicle due to a new sensor ID or change of wheel position of the sensors to ensure the trouble-free communication between sensor and TPMS receiver
- The self-assembly is made more difficult by these new technical requirements, which is why it is a good idea, to visit an expert/ a workshop for the tyre service
My car has no TPMS, must I install one retrospectively?
In the case of vehicles that are subject to a TPMS obligation, an indirect or direct TPMS was already fitted during manufacture, because otherwise this vehicle will be issued no type-approval or no approval within the EU member states.
A subsequent installation of a TPMS is not mandatory.
What happens if my TPMS does not work properly?
 A warning signal is shown in the display of the vehicle, a workshop should be visited as soon as possible, because either the TPMS is not working, or an air leak is present.
A warning signal is shown in the display of the vehicle, a workshop should be visited as soon as possible, because either the TPMS is not working, or an air leak is present.
During the main inspection according to section 29 of the German Road Traffic Licensing Act a defective TPMS is a minor fault, which however, due to its safety relevance must be corrected at once by the vehicle owner/keeper.
What should I do if my vehicle tells me a that I have a loss of pressure?
You should visit a workshop as soon as possible or park the vehicle and contact a breakdown service since there is a defective tyre and driving safety is not assured.
How can I maintain my TPMS?
The valves for the sensors are subject to normal wear and tear and therefore need to be maintained on a regular basis (recommendation: at each tyre change).
A workshop with TPMS service can carry out the maintenance.














![]()



 A warning signal is shown in the display of the vehicle, a workshop should be visited as soon as possible, because either the TPMS is not working, or an air leak is present.
A warning signal is shown in the display of the vehicle, a workshop should be visited as soon as possible, because either the TPMS is not working, or an air leak is present.